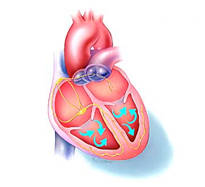
| Tachycardia is a too-fast heartbeat that may cause symptoms such as dizziness, palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, or syncope (fainting). If the heart beats too fast, there is not enough time between contractions for the ventricles to fill with a normal volume of blood. A very rapid heartbeat may also be irregular or chaotic. This is called fibrillation. Tachycardias are divided into two categories, depending on whether they arise in the upper or lower chambers of the heart. |
|
|
|
||
|
||
|
|
||
|
||
| Ventricular tachycardias often result from damage caused by a heart attack, cardiac surgery or other conditions that affect the ventricular muscle and the electrical conduction system that triggers the heartbeat. They can also result from rare, inherited heart defects. Sometimes, they occur in individuals who have no known heart condition. | ||
|